Battery Basics

Batteries are electrochemical devices that store chemical energy and convert it into electrical energy. They consist of one or more electrochemical cells that contain a positive electrode (cathode), a negative electrode (anode), and an electrolyte. The chemical reactions within the battery occur between the electrodes and the electrolyte, allowing the storage and release of energy.
Types of Batteries
Different types of batteries are categorized based on their chemical composition, construction, and applications. Each type has distinct characteristics and advantages, making them suitable for specific purposes.
- Lead-acid batteries are the oldest and most common type. They are widely used in vehicles, backup power systems, and deep-cycle applications. Lead-acid batteries consist of lead plates immersed in a sulfuric acid electrolyte. The chemical reactions involve the conversion of lead sulfate to lead oxide and lead during charging, and the reverse process during discharging. These batteries are known for their high power output, low cost, and durability but have a relatively short lifespan and are heavy.
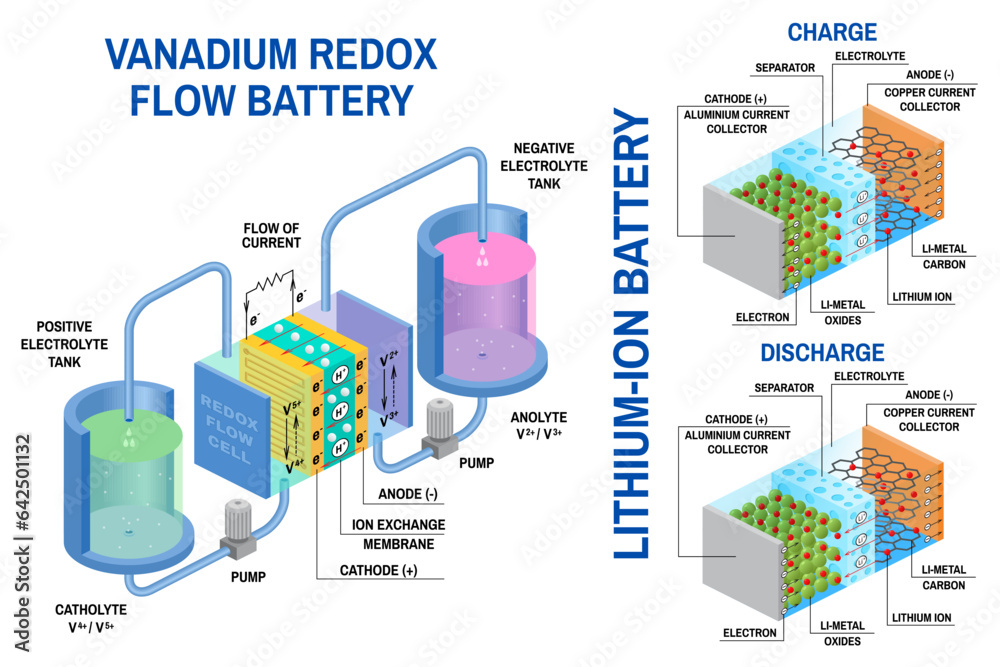
- Lithium-ion batteries have become ubiquitous in portable electronics, electric vehicles, and energy storage systems. They are known for their high energy density, lightweight design, and long lifespan. Lithium-ion batteries use lithium ions that move between the anode and cathode through an electrolyte. During charging, lithium ions are inserted into the anode material, while during discharging, they are extracted and move to the cathode. The anode materials typically consist of graphite or lithium metal oxides, while the cathode materials can be lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese oxide, or lithium iron phosphate.
- Alkaline batteries are commonly used in everyday devices such as flashlights, remote controls, and toys. They are known for their long shelf life and relatively low cost. Alkaline batteries use a zinc anode, a manganese dioxide cathode, and an alkaline electrolyte. During discharge, zinc reacts with the electrolyte to produce zinc oxide, while manganese dioxide is reduced to manganese oxide. These batteries are single-use and cannot be recharged.
Chemical Reactions in Batteries
The fundamental principle behind battery operation lies in the chemical reactions occurring within the cell. These reactions involve the transfer of electrons between the electrodes and the electrolyte, creating an electric current.
Charging
During charging, an external power source forces electrons to flow from the positive electrode to the negative electrode, reversing the chemical reactions that occur during discharge. This process involves the reduction of the cathode material and the oxidation of the anode material.
For example, in a lithium-ion battery, during charging, lithium ions are inserted into the anode material (graphite), while the cathode material (lithium cobalt oxide) is reduced.
Discharging
When a battery is discharged, electrons flow from the negative electrode to the positive electrode, generating an electric current. This process involves the oxidation of the anode material and the reduction of the cathode material.
In a lithium-ion battery, during discharge, lithium ions are extracted from the anode material and move to the cathode material, where they are inserted, causing the cathode to be reduced.
Battery Components

A battery is like a tiny power plant, storing chemical energy and converting it into electrical energy when needed. To understand how this works, we need to delve into the essential components that make up a battery. These components work together in a delicate dance, enabling the storage and release of energy.
Electrodes
Electrodes are the heart of a battery, where the chemical reactions that store and release energy take place. There are two main electrodes: the anode and the cathode.
The anode is the negative electrode, where oxidation occurs. Oxidation is a chemical process that involves the loss of electrons. In a battery, the anode releases electrons during discharge, creating a flow of electricity.
The cathode is the positive electrode, where reduction occurs. Reduction is the opposite of oxidation, involving the gain of electrons. During discharge, the cathode receives electrons from the anode, completing the electrical circuit.
The materials used for electrodes vary depending on the battery type. For example, lithium-ion batteries commonly use graphite for the anode and lithium cobalt oxide for the cathode. These materials are chosen for their electrochemical properties, which determine the battery’s performance and lifespan.
Electrolyte
The electrolyte is the conductor that allows ions to move between the electrodes. It is a liquid or solid material that can carry an electrical current. The electrolyte plays a crucial role in facilitating the chemical reactions within the battery.
During discharge, ions from the anode move through the electrolyte to the cathode, completing the circuit. During charging, the process reverses, with ions moving from the cathode to the anode.
The type of electrolyte used can significantly impact the battery’s performance and safety. For example, lithium-ion batteries often use a liquid electrolyte, which offers high conductivity but poses safety risks if the battery is damaged or overheated. Solid-state electrolytes are being explored as a safer alternative, offering improved safety and potentially longer lifespan.
Separator
The separator is a thin, porous membrane that physically separates the anode and cathode, preventing them from coming into direct contact. This separation is crucial for maintaining the battery’s stability and preventing short circuits.
The separator allows ions to pass through but blocks the flow of electrons, ensuring that the chemical reactions occur only at the electrodes. Different materials, such as polymers or ceramics, are used for separators, depending on the battery type and its operating conditions.
Casing
The casing is the protective outer layer that encloses the battery’s internal components. It provides structural support and protects the battery from external damage, such as impact, moisture, or heat.
The casing can be made from various materials, including metal, plastic, or ceramic, depending on the battery’s application and design requirements. The casing also plays a role in the battery’s thermal management, helping to dissipate heat generated during operation.
Battery Performance Metrics: What Is Battery
Understanding the performance of a battery is crucial for selecting the right battery for a specific application. Various metrics are used to evaluate battery performance, each providing insight into different aspects of the battery’s functionality.
Battery Capacity
Battery capacity refers to the amount of electrical charge a battery can store. It is typically measured in Ampere-hours (Ah) or milliampere-hours (mAh). A higher capacity battery can deliver more current for a longer duration.
Battery capacity is often referred to as the “C-rate,” which represents the rate at which the battery is discharged. A 1C discharge rate means the battery is fully discharged in one hour.
Battery Voltage
Battery voltage represents the electrical potential difference between the battery’s positive and negative terminals. It is measured in volts (V). The voltage of a battery determines the power it can deliver.
The voltage of a battery is determined by the chemical composition of the battery’s electrodes and electrolyte.
Battery Current
Battery current refers to the rate of flow of electrical charge through the battery. It is measured in amperes (A). The current a battery can deliver depends on its internal resistance and the load connected to it.
A higher current rating indicates a battery can deliver more power to a load.
Battery Energy Density
Battery energy density is a measure of the amount of energy stored per unit volume or mass. It is typically expressed in watt-hours per liter (Wh/L) or watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg).
A higher energy density battery can store more energy in a smaller space or lighter weight.
Battery Cycle Life
Battery cycle life refers to the number of charge-discharge cycles a battery can withstand before its performance degrades significantly. It is typically measured in cycles.
Cycle life is affected by factors such as the depth of discharge, temperature, and charge rate.
Factors Influencing Battery Performance Metrics, What is battery
Several factors can influence battery performance metrics, including:
- Battery chemistry: Different battery chemistries have varying performance characteristics. For example, lithium-ion batteries have higher energy density than lead-acid batteries but lower cycle life.
- Temperature: Battery performance is affected by temperature. High temperatures can accelerate degradation, while low temperatures can reduce capacity and power output.
- Charge and discharge rate: Charging and discharging a battery too quickly can reduce its cycle life and capacity.
- Depth of discharge: Deeply discharging a battery can shorten its cycle life.
- Age: Battery performance degrades over time, even if it is not used.
Battery Performance Characteristics Comparison
| Battery Type | Capacity (Ah) | Voltage (V) | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Cycle Life (Cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-acid | 50-200 | 12 | 30-40 | 300-500 |
| Lithium-ion | 1-100 | 3.6-4.2 | 150-250 | 500-1000 |
| Nickel-cadmium | 1-10 | 1.2 | 50-60 | 1000-2000 |
| Nickel-metal hydride | 1-10 | 1.2 | 60-80 | 500-1000 |
What is battery – Battery, in a legal context, refers to the unlawful use of force against another person. It can range from a simple push to a more serious assault. This concept is often in the news, especially when discussing celebrity relationships, like who is skai jackson boyfriend , as public figures can be subject to scrutiny and gossip.
Understanding the legal definition of battery is crucial to navigating these situations and ensuring that everyone’s rights are protected.
Battery is a legal term referring to an intentional act that causes harmful or offensive contact with another person. This can be physical, such as hitting or pushing, or it can be verbal, such as threats or intimidation. It’s important to understand that even without physical contact, words can still constitute battery if they cause a reasonable person to fear immediate harm.
For example, in the case of Skai Jackson and boyfriend , any aggressive or threatening behavior towards one another, even if not physically violent, could be considered battery depending on the specific circumstances. Understanding the nuances of battery can be helpful in navigating interpersonal conflicts and ensuring that everyone’s boundaries are respected.